SQL Server 2008에 새롭게 선보인 기능이다.
2 페이지 압축 – column-prefix #
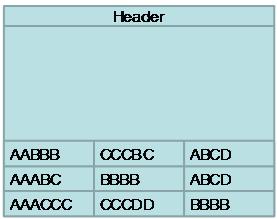
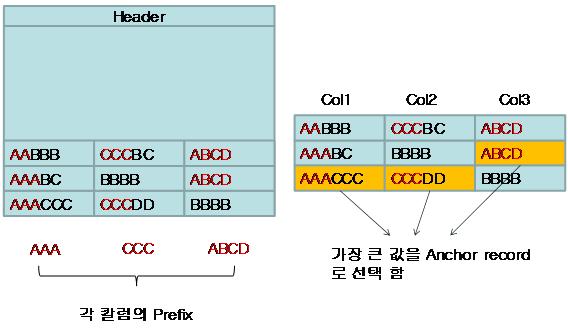
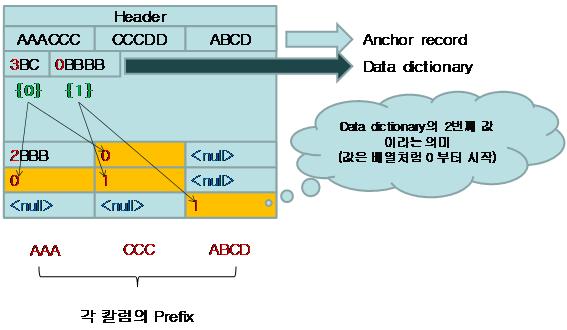
SQL Server는 하나의 column-prefix data를 새로운 레코드를 생성한다. 이 레코드를 anchor-record 라고 부른다. Anchor-recode는 페이지 헤더 다음에 저장된다. 만약 Common ‘byte’pattern 이 발견되지 못하면 empty 또는 null로 취급된다. 만약 column-prefix를 가지지 않는다면 Anchor-record는 생성되지 않는다. 다음의 그림과 같이 하나의 페이지에 레코드들이 저장되어 있다.
SQL Server는 각각의 컬럼에 대한 레코드를 읽고, Common ‘byte’pattern 룰에 의해서 Column-prefix를 찾는다.
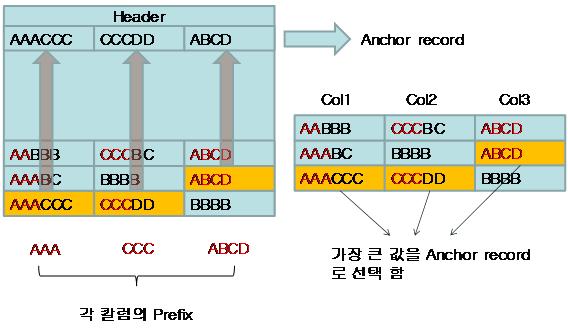
SQL Server는 Page Header 바로 다음에 Anchor-Record를 만든다.
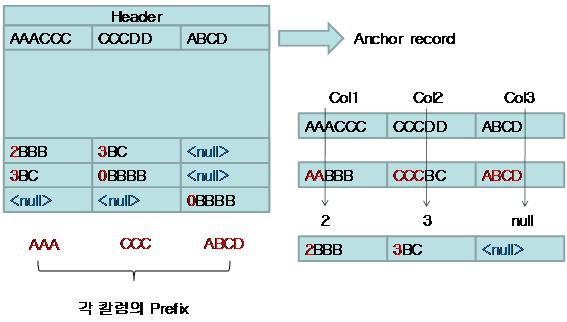
SQL Server는 Anhcor record를 다른 레코드로 취급한다. 그러므로 SELECT 쿼리로 조회가 불가능하다. SQL Server는 Anchor-record에 Column-prefix만 저장하지 않고, 가장 큰 데이터를 저장한다. 왜냐하면 그래야만 압축할 수 있는 데이터의 범위가 넓어지기 때문이다. 다음은 이런 과정을 거쳐서 페이지가 압축된 결과이다.
그림에서 압축된 데이터의 표현한‘2BBB’의 의미는 Anchor record 첫 번째 Column-prefix 인 ‘AAACCC’의 1~2번째 byte까지의 데이터가 같다는 의미이다. 예를 들어 첫 번째 컬럼에 대한 Anchor record의 첫 번째 컬럼의 값이 ‘AAAAAAAAAAAAAACC’일 때 레코드의 값이 ‘AAAAAAAAAAAAAA’라면 14로 표현하여 적어도 10byte이상은 줄일 수 있다.
압축률 조회
EXEC sp_estimate_data_compression_savings '스키마','테이블',NULL, NULL, 'PAGE'
EXEC sp_estimate_data_compression_savings '스키마','테이블', NULL, NULL, 'ROW'
동적관리함수
sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats 를 사용하여 물리적인 정보를 얻는다.
실제 예제
USE AdventureWorks2008;
GO
IF OBJECT_ID('dbo.temp') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.temp;
GO
SELECT A.*
INTO dbo.temp
FROM HumanResources.Employee a, HumanResources.Employee b, HumanResources.Employee c
GO
EXEC sp_spaceused 'dbo.temp';
/*
rows : 24389000
reserved: 4386456 KB
data : 4386392 KB
*/
ALTER TABLE temp
REBUILD
WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE)
GO
EXEC sp_spaceused 'dbo.temp';
/*
rows : 24389000
reserved: 297616 KB
data : 297432 KB
*/
7 DB의 모든 테이블 및 인덱스 압축하기 #
기본적으로 page 압축을 하며, 필요에 따라서 row 압축으로 수정하도록 하삼..모니터링은 다른 세션에서
tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A] 테이블을 조회하삼.. 압축 안한 인덱스 및 테이블만 압축한다.
set statistics io off
set nocount on
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]') is not null
drop table tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]
create table tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]
(
sql_str varchar(1000)
);
declare @tname varchar(500);
declare cur cursor for
select query
from (
select
'alter table ' + table_schema + '.' + table_name +
' rebuild with (data_compression = page, online=on)' query
, (select top 1 data_compression_desc
from sys.partitions
where object_id = object_id(table_schema + '.' + table_name)
and index_id = 0) compress --heap
from information_schema.tables
where table_name <> 'sysdiagrams'
and table_type = 'BASE TABLE'
union all
select
'alter index ' + b.name + ' on ' +
schema_name(a.uid) + '.' + a.name +
' rebuild with (data_compression = page, online=on)'
, (select top 1 data_compression_desc
from sys.partitions
where object_id = object_id(table_schema + '.' + table_name)
and rows >= 1000000 -- 1백만 건 이상만..
and index_id = b.index_id) compress
from sys.sysobjects a
inner join sys.indexes b
on a.id = b.object_id
inner join information_schema.tables c
on schema_name(a.uid) + '.' + a.name = table_schema + '.' + table_name
where c.table_name <> 'sysdiagrams'
and c.table_type = 'BASE TABLE'
and b.name is not null
) t
where compress = 'NONE' --압축한거는 제외하고, 압축 안한거만 압축한다.. 말이 우끼네..
open cur;
fetch next from cur into @tname;
while @@FETCH_STATUS not in (-1, -2)
begin
--exec(@tname);
print @tname;
insert tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A] values(@tname);
fetch next from cur into @tname;
end
close cur;
deallocate cur;
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]') is not null
drop table tempdb.dbo.[5E47F809-DACB-4918-B9EC-14CD495E3B3A]
8 압축여부 조회 #
파티션에 대한 정보는
테이블의 인덱스 및 파티션 정보보기 문서를 참고하라.
select * --data_compression_desc 컬럼 참고
from sys.partitions
where object_id = object_id('dbo.aaa')
drop table if exists #temp
select
concat(schema_name(schema_id), '.', name) table_name
, b.compression_cnt
, b.none_cnt
, b.rows
into #temp
from sys.objects a
cross apply (
select
count(case when data_compression_desc = 'NONE' then 1 end) none_cnt
, count(case when data_compression_desc <> 'NONE' then 1 end) compression_cnt
, sum(rows) rows
from sys.partitions
where object_id = a.object_id
) b
where a.type = 'u'
select * from #temp order by 1
9 파티션 압축 #
기본적으로 다음과 같이 한다.
ALTER TABLE PartitionTable1
REBUILD PARTITION = ALL
WITH (DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE ON PARTITIONS(1) ) ;
GO
ALTER TABLE PartitionTable1
REBUILD PARTITION = ALL
WITH
(
DATA_COMPRESSION = PAGE ON PARTITIONS(1),
DATA_COMPRESSION = ROW ON PARTITIONS(2 TO 4)
) ;
GO
스크립트도 만들어 보았다. 아래는 테이블 압축.
set nocount on
set statistics io off
declare
@bdt char(8)
, @edt char(8)
, @p int
, @sql varchar(4000)
set @bdt = '20110928'
while (@bdt <= '20300301')
begin
set @edt = convert(char(8), dateadd(dd, 1, @bdt), 112)
set @p = $partition.파티션함수(@bdt)
set @sql = '
alter table 테이블명
rebuild partition = ' + convert(varchar, @p) + '
with (data_compression = page)'
--exec (@sql)
print @sql
--print @bdt + ', ' + @edt
set @bdt = @edt
end
인덱스 압축
set nocount on
set statistics io off
declare
@bdt char(8)
, @edt char(8)
, @p int
, @sql varchar(4000)
set @bdt = '20111123'
while (@bdt <= '20121027')
begin
set @edt = convert(char(8), dateadd(dd, 1, @bdt), 112)
set @p = $partition.파티션함수(@bdt)
set @sql = '
alter index 인덱스명
on 스키마명.테이블명
rebuild partition = ' + convert(varchar, @p) + '
with (data_compression = page)'
--exec (@sql)
print @sql
--print @bdt + ', ' + @edt
set @bdt = @edt
end
필자의 테스트결과 일반적으로 page 압축이 좀 더 압축이 잘 되었다. 압축을 어떻게 하는지도 설명했다. 뭐.. 이런거 알면 뭐가 달라지나? 내가 압축 방법을 바꿀 수도 없는데 말이다. 아무래도 잊어버리는게 더 낫게다는 생각을 해본다.
데이터 중복에 의한 성능 문제를 해결하기 위한 방법 중에 원천적인 해결방법으로 정규화가 있다. 여의치 않다면 이런 압축기술이나 하드웨어에서 직접적으로 제공하는 데이터 중복 제거 기술을 이용하면 될 것이다. 이러한 솔루션은 사람을 1명 더 뽑는거 보다 어쩌면 더 효율적일 수도 있다..
![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) SQL Server 2008 Page Compression: Performance impact on table scans(http://sqlblog.com/blogs/linchi_shea/archive/2008/05/16/sql-server-2008-page-compression-performance-impact-on-table-scans.aspx)
SQL Server 2008 Page Compression: Performance impact on table scans(http://sqlblog.com/blogs/linchi_shea/archive/2008/05/16/sql-server-2008-page-compression-performance-impact-on-table-scans.aspx)![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Data Compression: Strategy, Capacity Planning and Best Practices(http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd894051.aspx)
Data Compression: Strategy, Capacity Planning and Best Practices(http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd894051.aspx)![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Row compression in SQL Server 2008(http://www.databasejournal.com/features/mssql/article.php/3822901/article.htm)
Row compression in SQL Server 2008(http://www.databasejournal.com/features/mssql/article.php/3822901/article.htm)![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Page compression in SQL Server 2008(http://www.databasejournal.com/features/mssql/article.php/3824566/article.htm)
Page compression in SQL Server 2008(http://www.databasejournal.com/features/mssql/article.php/3824566/article.htm)![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) A Unicode Compression example(http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlserverstorageengine/archive/2009/08/17/a-unicode-compression-example.aspx)
A Unicode Compression example(http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlserverstorageengine/archive/2009/08/17/a-unicode-compression-example.aspx)![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Unicode Compression in SQL Server 2008R2(http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlserverstorageengine/archive/2009/08/17/unicode-compression-in-sql-server-2008r2.aspx)
Unicode Compression in SQL Server 2008R2(http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlserverstorageengine/archive/2009/08/17/unicode-compression-in-sql-server-2008r2.aspx)![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Customer feedback on Data Compression(http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlserverstorageengine/archive/2009/08/17/customer-feedback-on-data-compression.aspx)
Customer feedback on Data Compression(http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlserverstorageengine/archive/2009/08/17/customer-feedback-on-data-compression.aspx)![[http]](/moniwiki/imgs/http.png) Update on data compression performance/space-savings and links to published white papers(http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlserverstorageengine/archive/2009/08/16/update-on-data-compression-in-sql-server-2008-rtm.aspx)
Update on data compression performance/space-savings and links to published white papers(http://blogs.msdn.com/sqlserverstorageengine/archive/2009/08/16/update-on-data-compression-in-sql-server-2008-rtm.aspx)